Raised flooring is a common access flooring system used in data centers and other facilities for cable management and underfloor air conditioning. There are two main types of raised floors – traditional raised floors and low profile raised floors. They differ in height, construction and applications.
What is Low Profile Raised Floor System?
A Low Profile Raised Floor System refers to a type of raised flooring solution designed to create a slightly elevated platform for accommodating utilities, cabling, and other services in a building. Unlike traditional raised floors, which have a higher profile and larger void space underneath the floor surface, low profile raised floor systems offer a reduced height, typically ranging from 2 inches (5 cm) to 6 inches (15 cm).
The main goal of low profile raised floor systems is to provide a raised platform while minimizing the overall height of the floor. This makes them suitable for applications where space constraints or limited vertical clearance are factors to consider. By utilizing lightweight materials and innovative construction methods, low profile raised floor systems can achieve their purpose without compromising on load-bearing capacity or structural integrity.
Low profile raised floor systems are often used in commercial office spaces, retail environments, conference rooms, and similar settings where moderate utility access is required. They may not be as suitable for applications like data centers or server rooms, which typically require traditional raised floors to accommodate heavy equipment and extensive cabling.
The advantages of low profile raised floor systems include:
1. Lower Height: Their reduced height makes them ideal for spaces with limited vertical clearance, creating a seamless transition between the raised floor and the surrounding flooring.
2. Aesthetic Appeal: Low profile raised floor systems offer a sleek and modern appearance, which can enhance the overall aesthetics of the space.
3. Easier Installation: The lower height and lighter materials can make the installation process more straightforward and potentially cost-effective.
4. Moderate Accessibility: While they may not provide as much space for utility access as traditional raised floors, low profile systems still offer reasonable accessibility for maintenance and reconfiguration.
What is Traditional Raised Floor System?
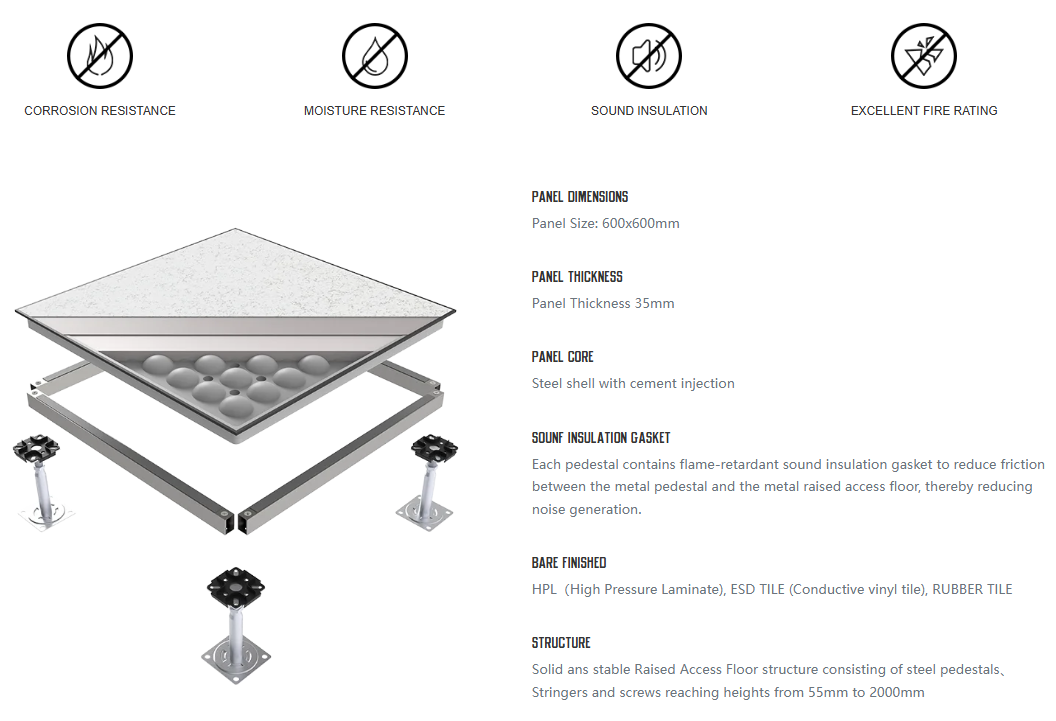
A Traditional Raised Floor System refers to a type of flooring construction used in buildings to create an elevated platform above the original floor level. This raised platform consists of a grid-like structure of pedestals and cross members, with panels placed on top to form the visible floor surface. The primary purpose of a traditional raised floor system is to accommodate utilities, cabling, and other services, allowing easy access for maintenance and reconfiguration.
Traditional raised floor systems are commonly used in buildings that require extensive cabling and utilities, such as data centers, server rooms, control rooms, trading floors, and laboratories. They provide ample space underneath the floor surface, making it easy to route and manage cables, cooling systems, power distribution, and other services.
The advantages of traditional raised floor systems include:
1. Excellent Accessibility: The ample space underneath the floor surface allows easy access for maintenance and modifications to utilities.
2. Cable Management: The raised floor provides a clean and organized space for routing and managing cables, reducing clutter and improving airflow.
3. Load-Bearing Capacity: Traditional raised floors are designed to support heavy equipment and large loads, making them suitable for critical infrastructure installations.
4. Flexibility: The modular nature of the floor panels allows for easy reconfiguration and future adaptability as the needs of the building change over time.
However, traditional raised floor systems also have some drawbacks, such as the need for a higher floor height and potential cost implications due to their more complex construction. As a result, alternative solutions like low profile raised floor systems have been developed to address certain space and design constraints while still providing a raised flooring solution.
Different Between Low Profile Raised Floor Systems vs Traditional Raised Floors
Low profile raised floor systems and traditional raised floors both serve the purpose of creating a raised platform to accommodate various utilities and cabling in buildings, but they have differences in design, height, construction, and applications. Here’s a comparison between the two:
1. Design and Height:
– Traditional Raised Floors: Traditional raised floors are typically constructed using metal pedestals and grid systems, with panels made of materials like steel, wood, or concrete. The height of these floors can range from 6 inches (15 cm) to several feet, depending on the requirements of the building and the complexity of the services running underneath.
– Low Profile Raised Floor Systems: Low profile raised floor systems, as the name suggests, have a lower height compared to traditional raised floors. They are designed to provide a minimal raised platform, usually ranging from 2 inches (5 cm) to 6 inches (15 cm). These systems often use innovative materials and construction techniques to achieve a lower profile while still accommodating utilities.
2. Construction and Materials:
– Traditional Raised Floors: Traditional raised floors are often constructed with heavy materials like steel or concrete. The panels used are relatively thick and robust, capable of supporting heavy loads and providing excellent structural integrity.
– Low Profile Raised Floor Systems: Low profile raised floors utilize lightweight materials and innovative construction methods to achieve their lower height. Common materials include aluminum, composite panels, or specialized plastics that are strong enough to support the intended loads while keeping the overall height to a minimum.
3. Load-Bearing Capacity:
– Traditional Raised Floors: Traditional raised floors are designed to support heavy equipment and large loads, making them suitable for data centers, computer rooms, and industrial applications where significant weight is involved.
– Low Profile Raised Floor Systems: Low profile raised floors have a reduced load-bearing capacity compared to traditional raised floors. They are ideal for commercial office spaces, retail environments, and areas with lighter equipment and cabling needs.
4. Accessibility and Flexibility:
– Traditional Raised Floors: Traditional raised floors offer greater accessibility since they provide more space underneath the floor surface, making it easier to install, reconfigure, and maintain cabling and utilities. However, this advantage comes with a higher height, which may not be suitable for certain spaces.
– Low Profile Raised Floor Systems: Low profile raised floors sacrifice some accessibility due to their reduced space underneath the floor surface. While they may be more challenging to reconfigure or add new utilities, their lower height can be an advantage in spaces with limited vertical clearance.
5. Applications:
– Traditional Raised Floors: Traditional raised floors are commonly used in data centers, IT server rooms, control rooms, and other settings where extensive cabling and equipment are necessary, and easy access is essential.
– Low Profile Raised Floor Systems: Low profile raised floors are better suited for general office spaces, retail environments, conference rooms, and similar settings where moderate utility access is required but maintaining a lower floor height is preferred.
Ultimately, the choice between low profile raised floor systems and traditional raised floors depends on the specific needs of the building and the intended applications. Each option has its advantages and limitations, and careful consideration of the requirements will help determine the most suitable solution.
Huiya Real-Time News
Huiya Real-Time News is dedicated to providing you with the latest and most authoritative information on the raised flooring industry.
We provide 24/7 updates on industry policy interpretations, market trend analysis, company news.
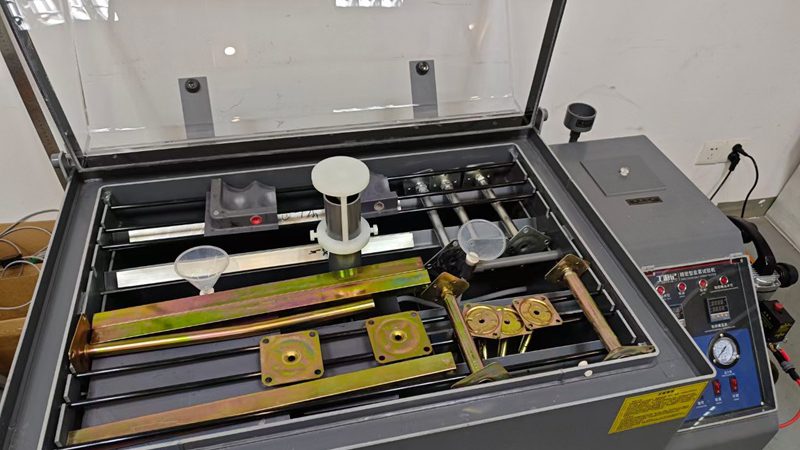

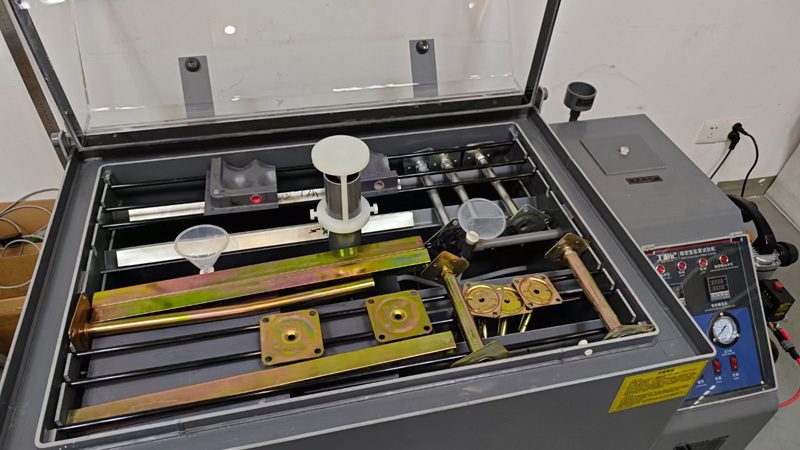
匯亜、新たに塩霧試験装置を導入 OAフロアの品質防線を強化
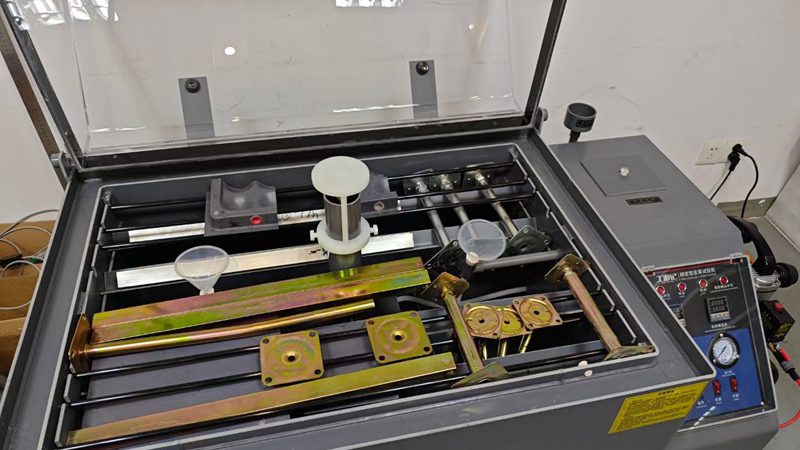

회아, 새 염무시험장비 도입해 이중바닥재 품질 방호선 단단히 만듦
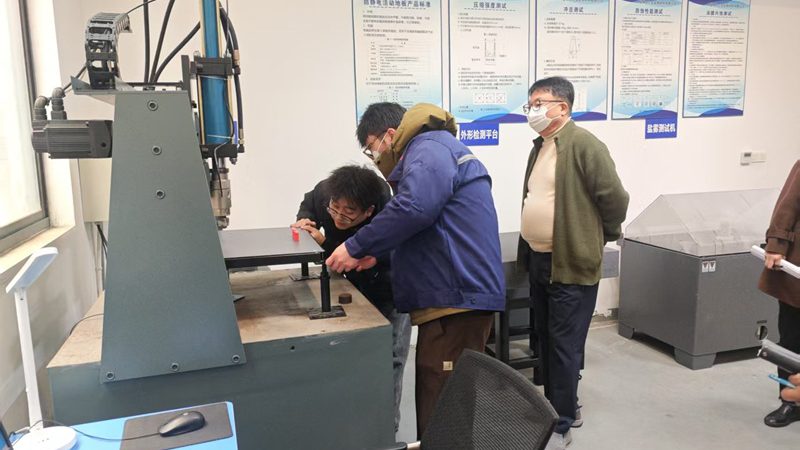

창주 회아 이중바닥재 회사, 한국 KSA 인증 획득하며 이중바닥재 공식 한국 수출 시작
MORE DOWNLOADS

GENERAL CATALOGUE

HUIYA INTRODUCTION

HUIYA GREEN LABEL
CAD/BIM FULL STEEL
APPLICATION SCENARIOS