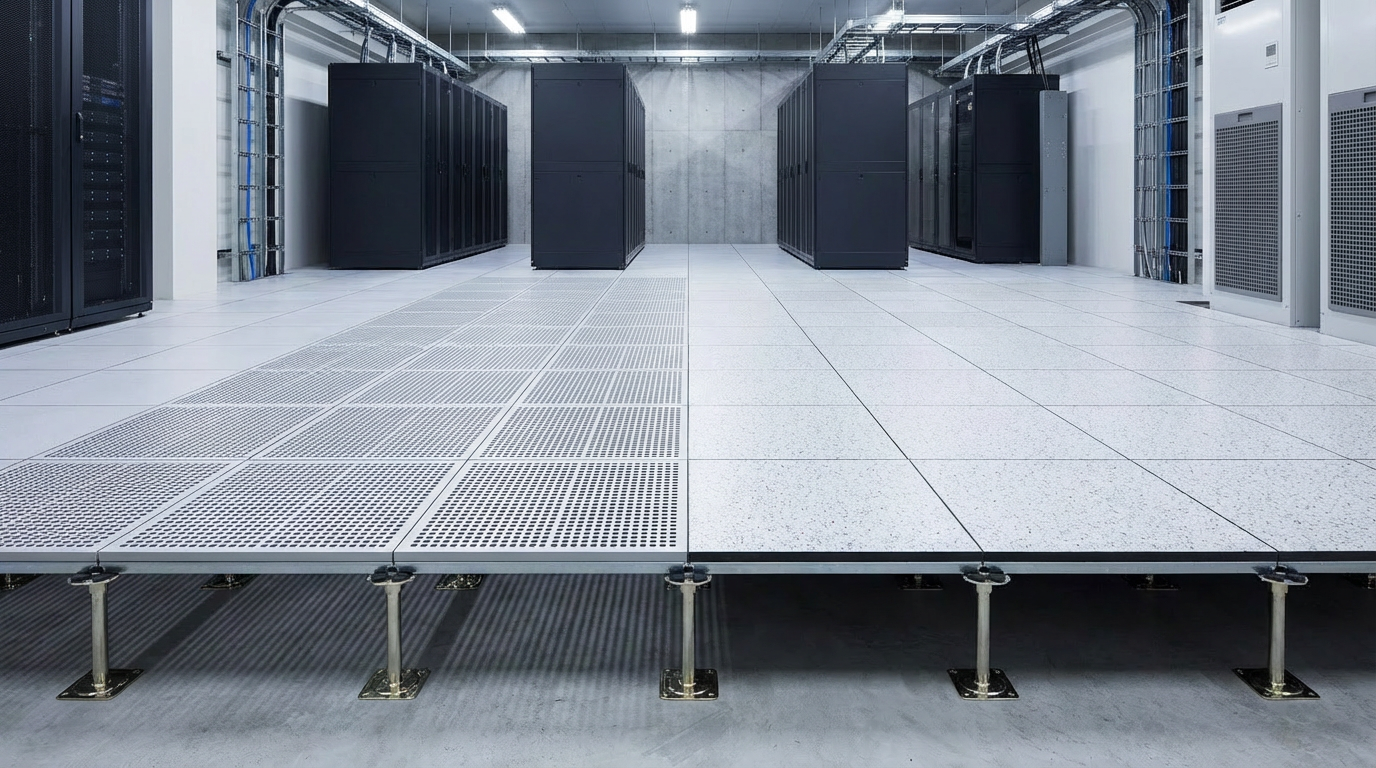
In the digital age, where data flows like a powerful current, every business needs a reliable and efficient server room to keep their operations afloat. It’s the beating heart of an organization’s IT infrastructure, safeguarding critical information and powering the technology that drives progress. But what are the secrets to creating a server room that ensures seamless functionality and robust security? Join us on an enlightening journey as we uncover the key requirements that transform a mundane server room into a powerhouse of technological excellence. From temperature control to backup power systems, from security measures to scalability, we’ll delve into the must-haves that make server rooms the nerve center of modern businesses. Get ready to unveil the hidden world of server room requirements and unlock the potential for unparalleled performance and peace of mind.

- Power and Cooling Requirements:
Power and cooling requirements are critical considerations when designing a server room to ensure the smooth and reliable operation of the servers. Here are some key factors to consider for power and cooling:
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS):
To protect against power outages, server rooms must be equipped with UPS systems. UPS units provide backup power during outages, preventing data loss, and allowing for an orderly shutdown of servers. Sizing the UPS units to handle the total power load and providing redundant UPS units ensure uninterrupted power supply.
Power Distribution and Redundancy:
Efficient power distribution is vital for managing server racks. Implementing intelligent power distribution units (PDUs) enables remote monitoring, load balancing, and power consumption tracking. Redundancy should be built into the power infrastructure, including redundant power feeds, circuit breakers, and backup generators.
Cooling Systems:
Servers generate significant heat, necessitating efficient cooling systems. Precision air conditioning units, in-row cooling, or liquid cooling solutions help maintain optimal temperatures. Proper airflow management, hot and cold aisle containment, and regular maintenance of cooling equipment are essential to prevent overheating and ensure server reliability.
Monitoring and Automation:
Implement environmental monitoring systems to continuously monitor the temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors within the server room. This allows for proactive management of cooling and power-related issues. Consider using automation and smart technologies to optimize cooling and power management based on real-time conditions.
Energy Efficiency:
Focus on energy-efficient equipment and cooling solutions to minimize power consumption and reduce environmental impact. Look for servers with high-efficiency power supplies, cooling systems with variable speed fans or pumps, and consider using technologies like virtualization to consolidate servers and reduce overall power requirements. - Environmental Considerations:
When setting up a server room, it is important to take into account environmental considerations to ensure the efficient and reliable operation of the servers and minimize their environmental impact. Here are some key environmental factors to consider:
Temperature and Humidity Control:
Maintaining an optimal temperature and humidity range is crucial for the reliable operation of servers. Recommended temperature ranges typically fall between 18-27 degrees Celsius (64-80 degrees Fahrenheit), with humidity levels around 40-60%. Implementing a robust HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system and monitoring tools enables real-time monitoring and automated adjustments to ensure optimal environmental conditions.
Air Filtration and Dust Control:
Airborne particles and dust can accumulate on server components, impacting performance and longevity. Server rooms should be equipped with air filtration systems and regularly cleaned to minimize dust buildup. This ensures that servers operate within their specified temperature ranges, reducing the risk of hardware failure.
Fire Suppression Systems:
Deploying fire suppression systems, such as clean agent or gas-based systems, is critical to safeguard server rooms. These systems can rapidly suppress fires without damaging sensitive equipment. Additionally, implementing smoke detectors and fire-resistant construction materials enhances overall fire safety. - Physical Security:
Physical security for a server room is crucial to protect the valuable equipment, data, and sensitive information stored within. Here are some important measures to consider:
Access Control:
Limit and control access to the server room. Implement a robust access control system that includes measures such as swipe cards, biometric authentication, or keypads. Restrict access only to authorized personnel, and maintain a log of individuals entering and leaving the room.
Locks and Doors:
Ensure that the server room has sturdy doors with high-security locks. Consider using reinforced doors with solid cores and install tamper-proof hinges and deadbolts. Restrict the number of access points and ensure they are properly secured.
Video Surveillance:
Install security cameras in strategic locations to monitor the server room and its surroundings. Ensure that the cameras cover all entry points and critical areas within the room. Keep the surveillance system operational and regularly review the footage.
Alarms and Sensors:
Implement an intrusion detection system that includes motion sensors, door/window sensors, and glass-break detectors. Connect these sensors to an alarm system that can alert security personnel or trigger a response in case of unauthorized access or attempted breach.
Environmental Controls:
Maintain proper environmental conditions within the server room to prevent equipment damage. Implement environmental monitoring systems to detect temperature, humidity, water leaks, and smoke. Set up alerts to notify staff in case of any abnormal conditions.
Fire Suppression Systems:
Install fire suppression systems, such as automatic sprinklers or clean agent suppression systems, to extinguish fires effectively without causing further damage to the equipment. Regularly inspect and maintain these systems to ensure their proper functioning.
Secure Racks and Cabinets:
Secure server racks and cabinets with locks to prevent unauthorized access and tampering with equipment. Use cable management systems to ensure tidy and organized cabling, which also helps in identifying any unauthorized changes or additions.
Physical Barriers:
Consider implementing physical barriers like fencing, security gates, or security cages around the server room to restrict access further. These barriers can deter unauthorized individuals from attempting to gain entry.
Security Signage:
Clearly display signs indicating that the server room is a restricted area, and access is limited to authorized personnel only. Use warning signs to remind individuals of the consequences of unauthorized access or tampering.
Regular Audits and Maintenance:
Conduct regular audits of physical security measures, including access logs, surveillance footage, and equipment functionality. Perform maintenance checks on locks, alarms, sensors, and fire suppression systems to ensure they are operational and up to date.
Remember, physical security should be supplemented by robust cybersecurity measures, including network security, strong passwords, encryption, regular backups, and employee awareness training, to create a comprehensive security strategy for your server room. - Redundancy and Scalability:
When it comes to ensuring redundancy and scalability for a server room, there are several important factors to consider. Here are some key aspects to focus on:
Redundant Power Supply:
Implementing redundant power supply is crucial to ensure uninterrupted operation of your server room. This involves using multiple independent power sources, such as separate power grids or backup generators, along with automatic transfer switches (ATS) to seamlessly switch between them in case of a power outage.
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS):
A UPS provides temporary power during short-term power outages and acts as a buffer while the backup power source (e.g., generator) kicks in. UPS units typically incorporate batteries or flywheel energy storage to ensure a continuous power supply, giving you time to shut down systems gracefully or switch to backup power.
Redundant Networking:
Implementing redundant network connections is crucial to maintain connectivity in the event of a network failure. This can involve using multiple internet service providers (ISPs) with diverse network paths and utilizing technologies like link aggregation (e.g., EtherChannel or LACP) to combine multiple network links for increased bandwidth and redundancy.
Server Redundancy:
Employing redundant servers is essential for high availability. You can implement technologies like clustering or load balancing to distribute the workload across multiple servers. This way, if one server fails, the others can take over seamlessly, ensuring continuous service availability.
Storage Redundancy:
Redundant storage solutions, such as RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks), can protect against data loss by distributing data across multiple drives in different configurations. RAID levels like RAID 1 (mirroring) or RAID 5 (striping with parity) provide fault tolerance and improved read/write performance.
Scalable Infrastructure:
Designing a server room with scalability in mind enables you to accommodate future growth and increasing demands. Consider using modular designs that allow for easy expansion of server racks, network switches, and storage arrays. Virtualization technologies can also aid scalability by providing the flexibility to add or remove virtual machines as needed.
Environmental Controls:
Ensure proper environmental controls to maintain optimal operating conditions. This includes cooling systems, temperature and humidity monitoring, fire suppression systems, and physical security measures like access controls and surveillance.
Monitoring and Management:
Implement robust monitoring and management systems to oversee the server room infrastructure. This includes network monitoring tools, environmental sensors, power monitoring, and centralized management platforms to identify potential issues and proactively address them. - Best Practices for Efficient Server Room Management:
Efficient server room management is crucial for maintaining the reliability and performance of your IT infrastructure. Here are some best practices to consider:
Design and layout:
– Plan the layout of your server room to optimize space and airflow. Ensure adequate space between racks for easy access and proper cooling.
– Use cable management solutions to organize and label cables, minimizing clutter and simplifying maintenance.
– Consider implementing hot and cold aisles to separate the intake and exhaust airflows, improving cooling efficiency.
Environmental monitoring:
– Install temperature and humidity sensors to monitor environmental conditions in real-time. Set up alerts to notify you of any anomalies that could affect equipment performance.
– Implement fire detection and suppression systems to protect against potential fire hazards.
Cooling and ventilation:
– Use efficient cooling systems such as precision air conditioning units or in-row cooling to maintain optimal temperatures.
– Regularly clean and inspect cooling equipment, including air filters, to prevent dust buildup and maintain proper airflow.
– Use blanking panels and seal any gaps in server racks to prevent hot air recirculation and improve cooling efficiency.
Power management:
– Implement uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems to provide backup power during outages and protect against power fluctuations.
– Use power distribution units (PDUs) to manage and monitor power usage at the rack level, allowing for better capacity planning and energy efficiency.
– Consider implementing power management software to track power consumption and identify potential energy-saving opportunities.
Security:
– Control physical access to the server room with secure entry systems, including biometric authentication, access cards, or keypads.
– Install surveillance cameras to monitor the server room and record any unauthorized access or suspicious activities.
– Implement environmental sensors to detect water leaks and other potential hazards.
Documentation and labeling:
– Maintain up-to-date documentation of your server room, including equipment inventory, network diagrams, and cable layouts.
– Label all equipment, cables, and connections for easy identification and troubleshooting.
– Keep a record of maintenance activities, repairs, and equipment upgrades for future reference.
Regular maintenance and testing:
– Establish a regular maintenance schedule for server room equipment, including cleaning, inspections, and equipment updates.
– Conduct regular tests of backup power systems, cooling infrastructure, and environmental monitoring to ensure their effectiveness.
– Perform regular software and firmware updates on servers, switches, and other network equipment to ensure security and performance.
Disaster recovery and business continuity:
– Develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan that includes off-site backups, data replication, and redundant systems.
– Test your disaster recovery plan periodically to ensure its effectiveness and make necessary adjustments.
– Establish a business continuity plan to minimize downtime in the event of a disaster or system failure.
Remember that server room management practices may vary depending on the specific requirements of your organization. It’s important to continually assess and optimize your server room management strategy based on industry best practices and evolving technology.
Designing and maintaining a server room that meets the essential requirements of efficiency, reliability, and scalability is paramount for any organization’s IT infrastructure. Implementing environmental controls, power and cooling systems, physical security measures, redundancy, and scalability considerations ensures the smooth and uninterrupted operation of servers. By adhering to best practices for efficient server room management, organizations can optimize their server infrastructure and enhance the overall reliability and performance of their IT systems.
Huiya Real-Time News
Huiya Real-Time News is dedicated to providing you with the latest and most authoritative information on the raised flooring industry.
We provide 24/7 updates on industry policy interpretations, market trend analysis, company news.
MORE DOWNLOADS

GENERAL CATALOGUE

HUIYA INTRODUCTION

HUIYA GREEN LABEL
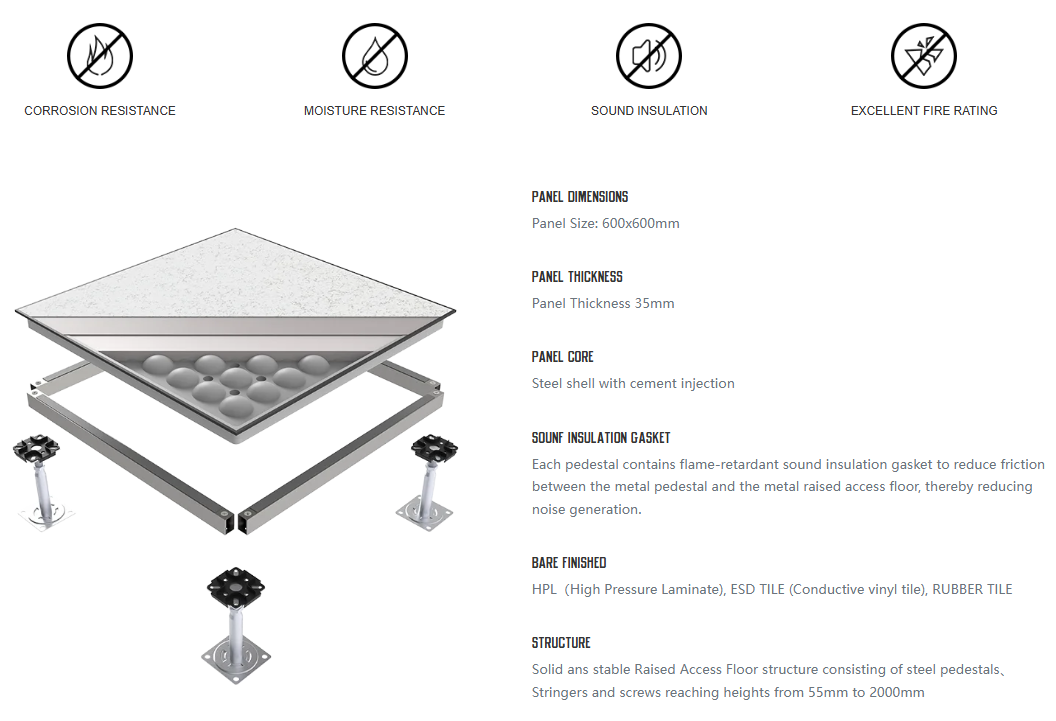
CAD/BIM FULL STEEL
APPLICATION SCENARIOS