With the continuous advancement of modern technology, electronic devices have assumed an increasingly vital role in both daily life and work environments. However, this progress has also brought attention to the widespread issue of electrostatics. Particularly in settings with high sensitivity to electronic equipment, such as data centers and laboratories, electrostatic problems can lead to severe consequences including equipment damage, data loss, and even fire hazards. To effectively address this issue, the proper grounding of electrostatic discharge (ESD) through raised access flooring emerges as paramount. This article breaks down the necessity of grounding raised access floors and provides step-by-step guidance on their effective grounding, aiming to offer readers valuable insights into the generation and resolution of electrostatic challenges.

The Necessity of Grounding Raised Access Floors
Raised access flooring, as a specialized flooring material, finds its primary application in places like electronic equipment facilities, computer server rooms, and laboratories. It effectively mitigates electrostatic buildup and discharge, safeguarding both equipment and personnel. However, a mere installation of raised access flooring cannot entirely eliminate ESD concerns. In specific environments, electrostatic charges might accumulate between devices, leading to adverse outcomes. Grounding, in such instances, offers a safe channel for the dissipation of accumulated electrostatic charges, thereby maintaining equipment functionality. Much like the “ground wire” in electrical systems, grounding of raised access flooring plays a pivotal role in electrostatic management, providing a suitable pathway for electrostatic discharge, and ensuring equipment and personnel safety.
Achieving Effective Grounding of Raised Access Floors: Step-by-Step
The effective grounding of raised access flooring is critical to preventing equipment damage, data loss, and fire hazards stemming from electrostatic problems. The following steps provide a comprehensive guide to grounding raised access floors.
Step 1: Preparation and Safety Considerations
Prior to initiating the grounding process, thorough preparation and safety measures are imperative. This entails acquiring necessary tools and materials such as conductive grounding wires, grounding rods, and grounding clamps. Simultaneously, ensuring the work area is devoid of combustible materials and other safety hazards is crucial to prevent mishaps.
Step 2: Selection of Appropriate Grounding Equipment
Select suitable grounding equipment based on the specific circumstances. Common grounding equipment includes:
– Grounding conductors: Well-conductive wires used to guide electrostatic charges to the ground. Copper wires, renowned for their superior conductivity and durability, are often employed.
– Grounding rods: Metal rod-like devices inserted into the ground to effectively guide electrostatic charges. These rods are typically fashioned from highly conductive metals such as copper or aluminum.
Step 3: Determining Grounding Locations
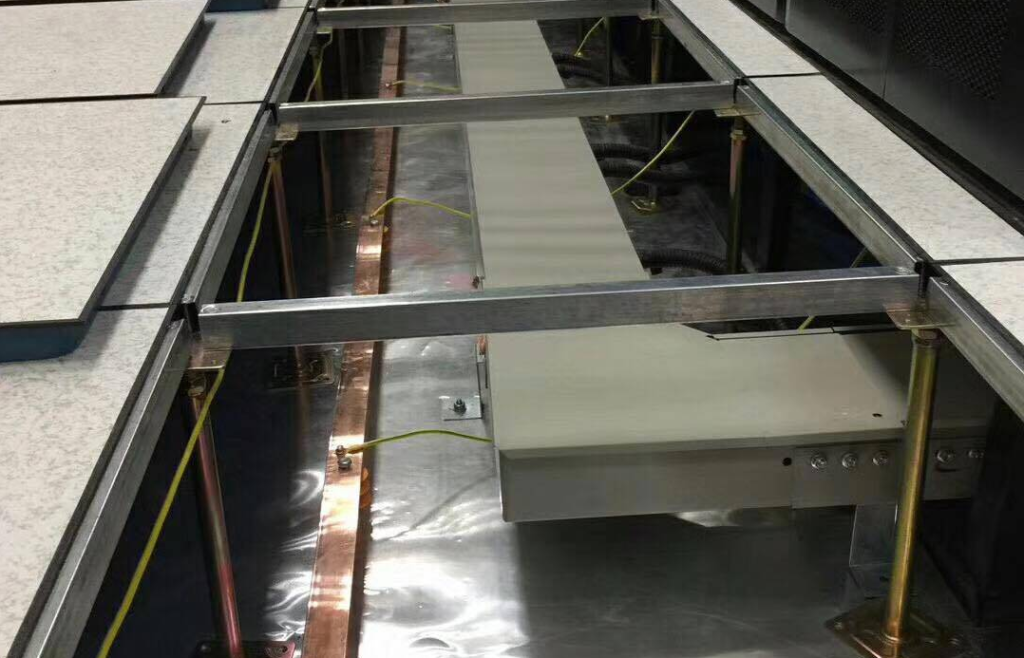
Within the layout of raised access flooring, identifying appropriate locations for installing grounding equipment is essential. Generally, grounding equipment should be evenly distributed throughout the entire raised access flooring system to ensure swift transmission of electrostatic charges.
Step 4: Connecting Grounding Equipment
Establish connections between grounding conductors or rods and the raised access flooring system. Ensuring secure and highly conductive connections is vital. One end of the conductor or rod should be linked to the raised access floor, while the other end connects to the ground.
Step 5: Ensuring Connection Quality
The quality of connections significantly impacts grounding effectiveness. Employ well-conductive connection components like grounding clamps to guarantee a secure and reliable link between the conductor or rod and the raised access floor. Loose or poor connections can lead to diminished grounding effects or complete failure.
Step 6: Testing Grounding Effectiveness
Upon completing grounding equipment connections, evaluate grounding effectiveness. Employ specialized testing equipment, such as an earth resistance tester, to measure the system’s resistance. Lower resistance values indicate improved grounding. Elevated resistance values might denote connection issues requiring prompt investigation and resolution.
Step 7: Regular Inspection and Maintenance
Consistent testing and maintenance are vital for the grounding system’s efficacy. Periodically employ an earth resistance tester to test the stability and effectiveness of the grounding system. Concurrently, regularly inspect the tightness of connection points, equipment condition, and the integrity of conductors.
Effective Maintenance Post Grounding of Raised Access Floors
The maintenance of grounded raised access floors is pivotal for the sustained operation of the grounding system. Regular inspections and maintenance aid in the timely detection and resolution of potential issues, ensuring the reliability of electrostatic prevention measures. Here are the maintenance steps and considerations following the grounding of raised access floors:
- Periodically Measure Grounding Resistance: Regularly measure the grounding system’s resistance using specialized earth resistance testing equipment. Lower resistance values indicate effective grounding, while an increase might signify connection issues or equipment damage.
- Inspect Connection Points: Regularly inspect the tightness and condition of grounding conductors, grounding rods, and associated connection points. Loose connections can compromise grounding effectiveness.
- Monitor Equipment Status: Monitor the operational status of equipment connected to raised access flooring. Identify any anomalies, as electrostatic-related issues could be the cause and necessitate further investigation.
- Handling Equipment Movement: When relocating or altering equipment on raised access flooring, ensure that the grounding system is not compromised. After equipment relocation, reassess the integrity of grounding connections.
- Maintenance Tasks: If maintenance tasks, such as cleaning or repairs, are necessary for raised access flooring, take care to preserve the integrity and effectiveness of the grounding system.
- Incorporating New Equipment: When integrating new equipment into the raised access flooring system, ensure that new devices are properly connected to the grounding system to maintain overall electrostatic prevention effectiveness.
- Maintain Humidity Levels: Maintaining appropriate indoor humidity levels helps reduce electrostatic generation. If the environment is excessively dry, consider employing humidifiers to maintain humidity levels.
- Training and Awareness: Provide training for individuals using the raised access flooring system, raising awareness about electrostatic prevention. Educate users about proper operational and maintenance procedures.
- Managing Emergency Situations: In the event of emergencies triggered by electrostatic issues, such as fires, ensure that emergency response teams are knowledgeable about proper procedures to minimize losses.
- Regular Maintenance Records: Establish maintenance records documenting maintenance dates, tasks performed, and outcomes. These records aid in tracking system health and devising sensible maintenance plans.
- Professional Assessment: Regularly engage professional technicians to comprehensively assess and evaluate the grounding system’s operation and effectiveness, ensuring alignment with expectations.
Maintaining grounded raised access floors demands continuous attention and patience to guarantee system stability and reliability. Regular maintenance efforts help preempt electrostatic problems, ensuring the safety of equipment and personnel, and prolonging the raised access floor system’s service life.
Huiya Real-Time News
Huiya Real-Time News is dedicated to providing you with the latest and most authoritative information on the raised flooring industry.
We provide 24/7 updates on industry policy interpretations, market trend analysis, company news.
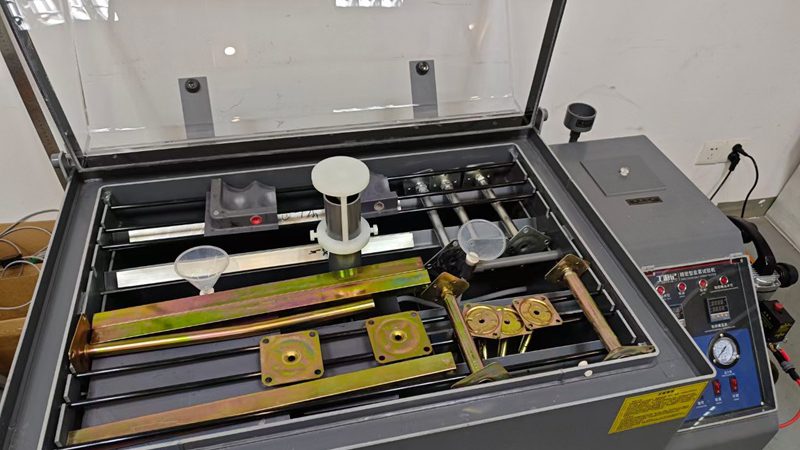

匯亜、新たに塩霧試験装置を導入 OAフロアの品質防線を強化
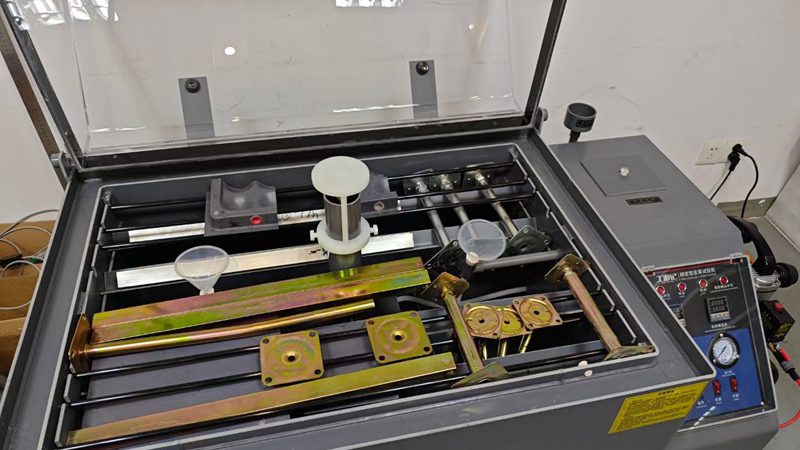

회아, 새 염무시험장비 도입해 이중바닥재 품질 방호선 단단히 만듦
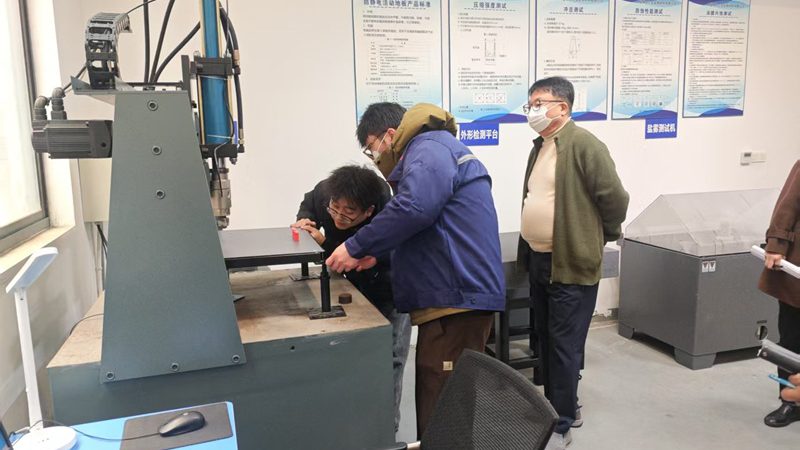

창주 회아 이중바닥재 회사, 한국 KSA 인증 획득하며 이중바닥재 공식 한국 수출 시작
MORE DOWNLOADS

GENERAL CATALOGUE

HUIYA INTRODUCTION

HUIYA GREEN LABEL
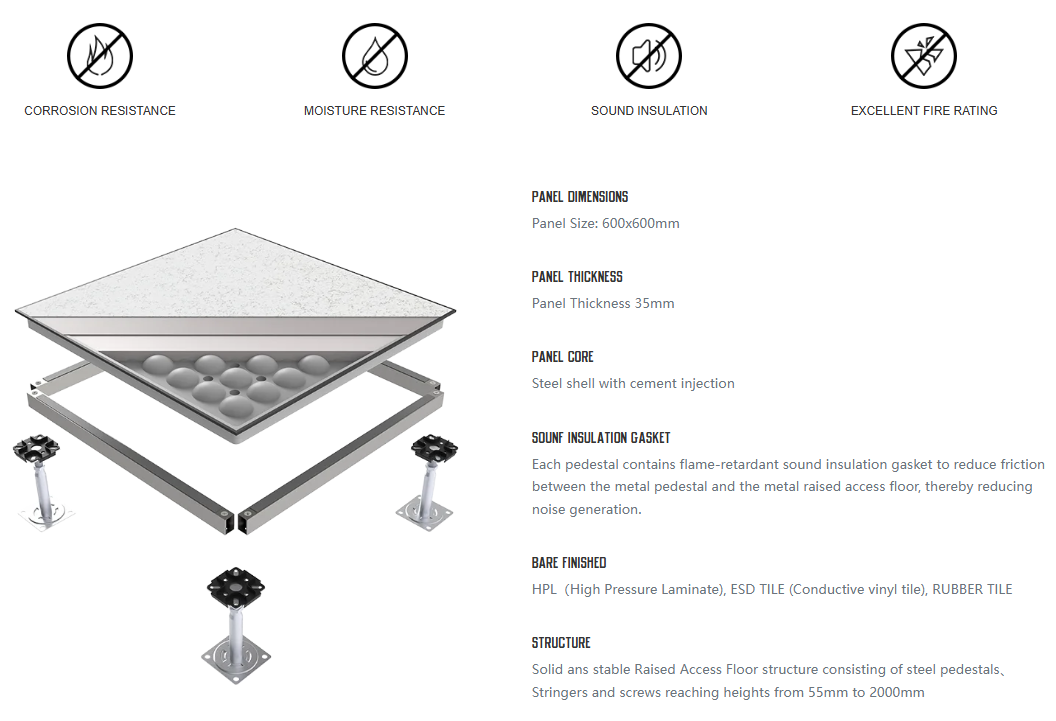
CAD/BIM FULL STEEL
APPLICATION SCENARIOS