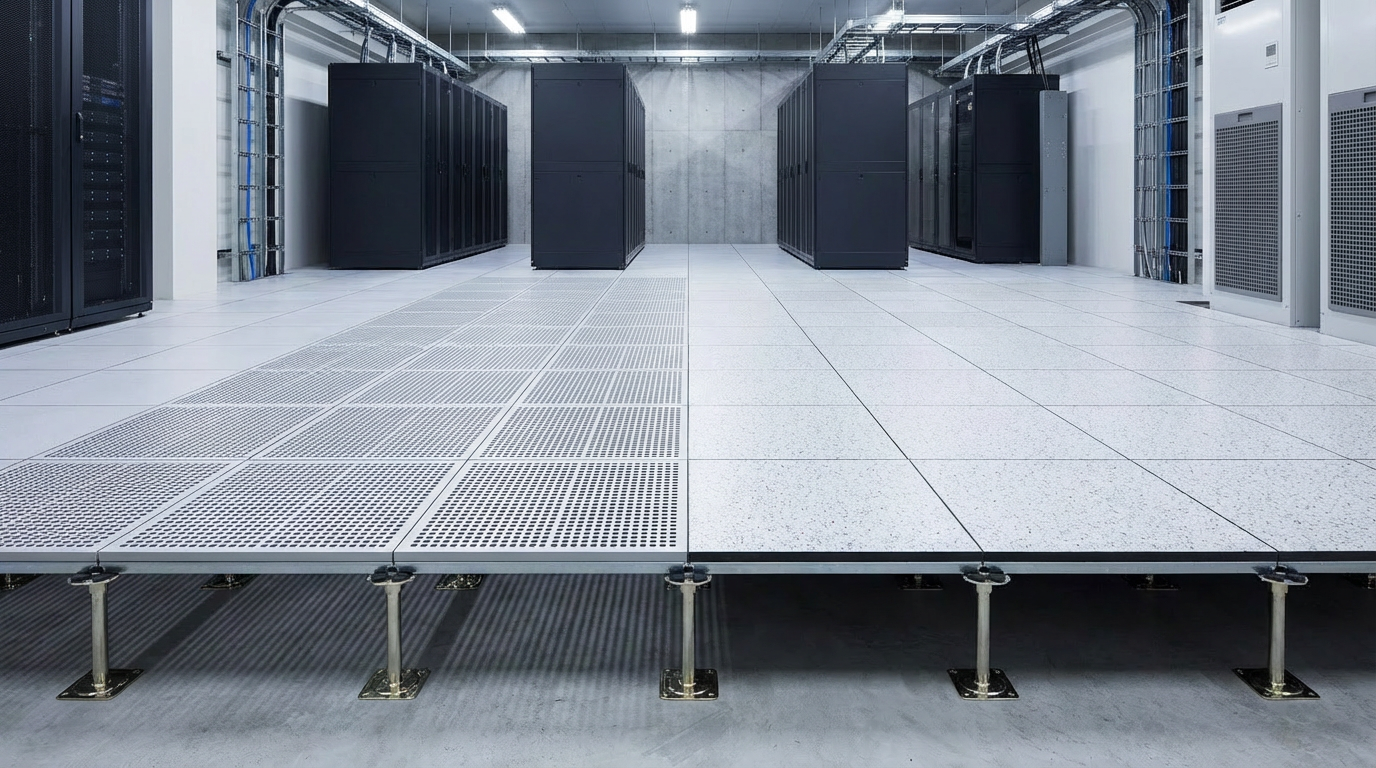
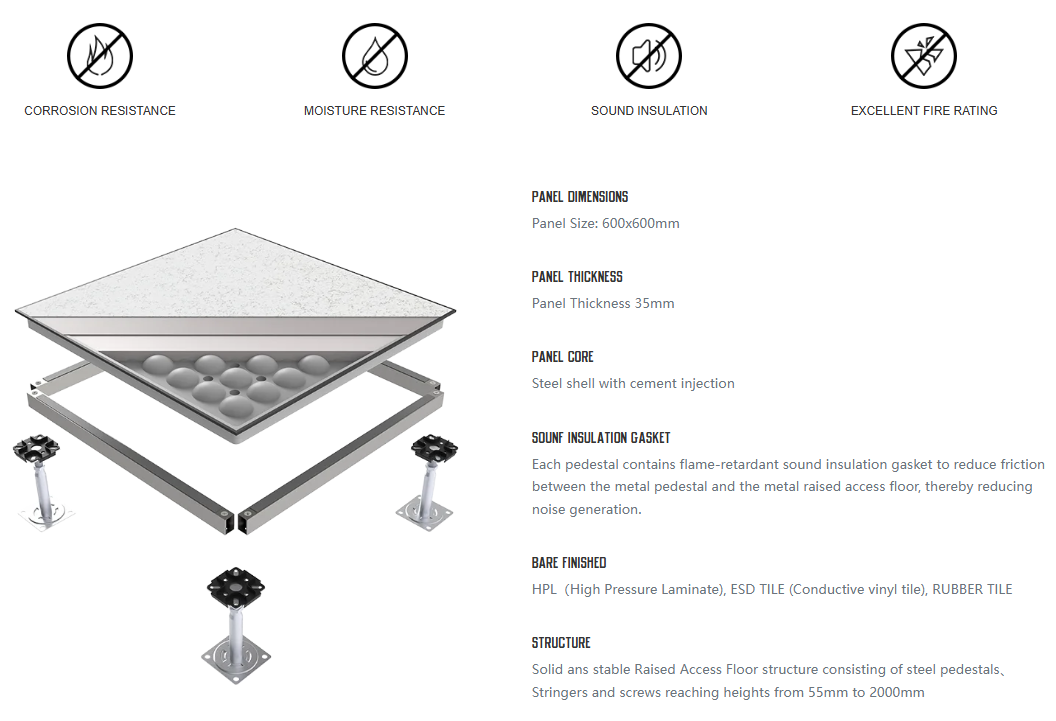
Raised floors are widely used in various settings, including offices, data centers, and commercial buildings through a variety of panel materials, flooring finishes, and installation methods. With this blog, HUIYA Raised Floor experts discuss with you the types of access floors, to help you choose an efficient flooring solution for your project and make the most ideal choice!!
Raised Floor System Types – Access Floor Tile Materials, Flooring Finishes, Installation Methods, Applications
Raised floors, also known as access floors, false floors, or technical floors, play a pivotal role in modern building infrastructure by providing an elevated structural floor above a solid substrate, such as a concrete slab. This design creates a hidden void for the passage of mechanical and electrical services, offering flexibility, functionality, and aesthetic integration. Here, we explore the different types of raised floors, focusing on the core materials and finishes, installation methods, and applications.
Raised Floor Panel Types (Tile Materials & Finishes)
Core Materials of Raised Access Floor Tiles
Raised floor panels come in various core materials, each tailored to meet specific environmental and structural demands:
1. All Steel Panels
Made entirely of steel, these panels are lightweight yet strong, featuring an epoxy finish for enhanced durability and protection. They are completely non-combustible and provide excellent grounding and electrical continuity.
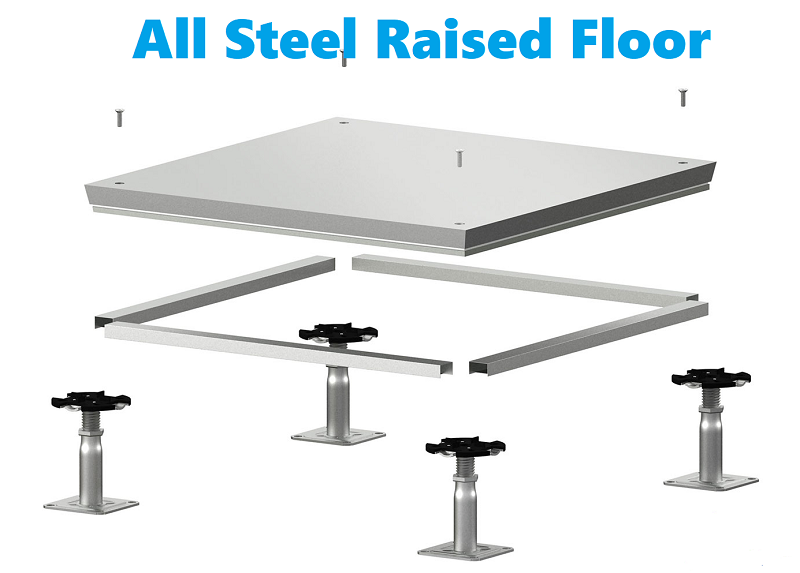

Benefits: Superior design load performance makes these panels ideal for environments that demand robust support and high safety standards, such as data centers and industrial facilities.
Fire Safety: Classified with a Class A rating for flame spread and smoke development.
2. Concore Panels
These panels are known for their excellent rolling load performance and ultimate load capabilities. Like all steel panels, they also feature an epoxy finish and are non-combustible.

Benefits: The solid and quiet nature of Concore panels makes them suitable for libraries, theaters, and other areas where noise reduction is beneficial.
Fire Safety: They maintain a Class A flame spread and smoke development rating, ensuring safety in fire-prone environments
3. Woodcore Panels
Economical and durable, Woodcore panels consist of a high-density particleboard core encased in a galvanized steel shell, which helps prevent zinc whiskers.

Benefits: These panels combine affordability with decent performance, making them a good choice for offices and educational institutions where heavy equipment is not used.
Fire Safety: They achieve a Class A rating in flame spread and smoke development, enhancing their suitability for public spaces.
3. Aluminum Panels
Aluminum panels are free of ferrous materials, which is crucial in environments sensitive to magnetic interference. They are lightweight and can be equipped with various static-dissipative coverings.
Benefits: Ideal for use in MRI rooms or data centers where interference with magnetic fields must be avoided. Their lightweight nature facilitates easy handling and installation.
Cost Consideration: These are generally the most expensive option due to their specialized applications and material costs.
4. Perforated Panels
Designed with small holes, perforated panels enhance airflow across the raised floor system, which is crucial for temperature regulation and minimizing hot spots.

Benefits: These panels are essential in data centers and server rooms where efficient cooling is critical. They help maintain optimal HVAC efficiency and are customizable to specific airflow needs.
Compatibility: Easily integrated into existing raised floor systems, making them ideal for upgrades or retrofits.
5. Chipboard Core Panels
Typically made from compressed wood particles, chipboard cores are cost-effective and widely used in environments that do not require heavy load-bearing capabilities but still need a stable and functional raised floor solution. The chipboard is often coated or covered to enhance its moisture resistance and durability.
6. Calcium Sulfate Panels
A denser and more durable option, calcium sulfate cores provide excellent fire resistance and superior acoustic insulation. This material is non-combustible, making it a safer choice in buildings where fire safety is a priority. It is also resistant to mold and mildew, which can be beneficial in humid environments.

7. Pressed Cement Aggregate Panels
Ideal for outdoor use or in areas where extreme durability and moisture resistance are required. This core type integrates natural stone aggregates, making it robust against physical and environmental stressors. It is exceptionally stable and suitable for high-traffic areas.
Finishes of Raised Access Floor Tiles
The finish of a raised floor not only contributes to its appearance but also its functionality and area of use:
1. Ceramic and Porcelain
These materials are hard-wearing and capable of withstanding a lot of foot traffic without showing much wear. They are easy to clean and maintain, making them ideal for public spaces, lobbies, and commercial environments where design impact is crucial.

2. PVC
Flexible and versatile, PVC finishes come in numerous designs and can mimic textures like wood, stone, or metal. This material is particularly useful in areas needing static control, such as data centers or electronic manufacturing facilities.
3. Vinyl Tiles
Known for their durability and resistance to moisture and stains, vinyl tiles come in a range of designs, including options that mimic wood or stone. Suitable for hospitals, schools, and areas requiring easy cleaning and maintenance.

4. Wood Tiles
Wood finishes provide a classic and warm appearance, enhancing the visual appeal of executive spaces, conference rooms, and corporate environments. But Wood tiles require maintenance to protect from moisture and wear.
5. Carpet Tiles
Softens the acoustics of a room, reduces noise levels, and adds comfort underfoot. It’s particularly favored in office environments where noise reduction can improve the work atmosphere. Commonly used in office environments and meeting rooms where a warm, inviting atmosphere is desired.
6. Linoleum Tiles
Linoleum floor is made from natural materials, linoleum tiles are environmentally friendly and available in a variety of colors and patterns. Ideal for eco-conscious buildings such as green-certified offices and educational facilities.
7. High Pressure Laminate (HPL) Tiles
Constructed under high pressure and heat, HPL tiles are extremely durable and resistant to scratches and stains. Perfect for high-traffic areas such as entryways and corridors in commercial buildings.
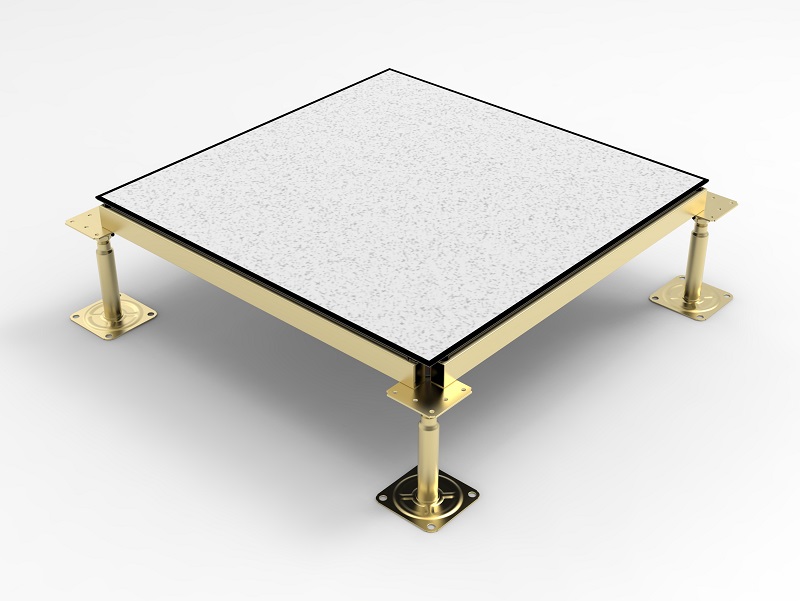
8. Rubber Tiles
Rubber offers slip resistance and shock absorption, making them durable and easy to clean. Frequently used in gyms, laboratories, and industrial areas where safety and comfort are priorities.
Choosing the right type of raised access floor involves considering the specific needs of the space, including load requirements, fire safety, electrical continuity, and aesthetic preferences.
Raised Access Floor Installation Types
Raised floor systems offer versatility not only in terms of materials and finishes but also through various installation methods. Each method caters to different environmental needs, structural requirements, and specific applications. Here’s an overview of the common types of raised floor installations:
1. Traditional Raised Floor
Characterized by a greater clearance between the subfloor and the floor panels, traditional raised floors are designed to accommodate extensive cabling, HVAC systems, and other necessary infrastructures beneath the floor.
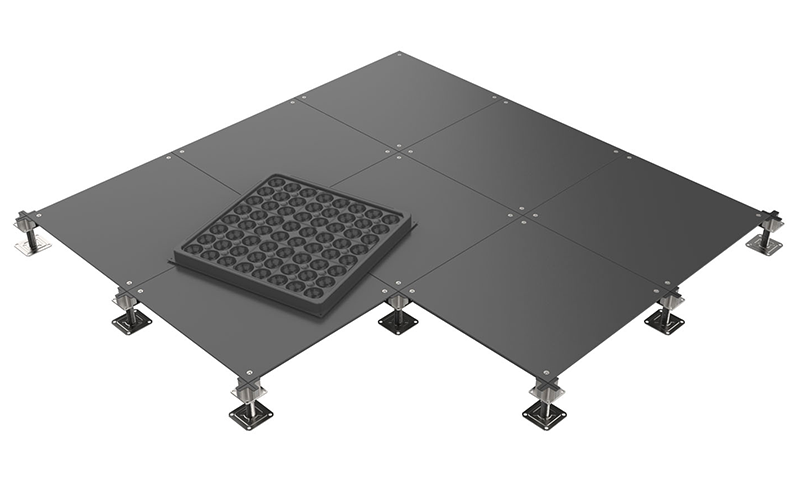
Height: Typically, the void between the subfloor and the bottom of the panels is more than 6 inches, providing ample space for HVAC systems, electrical wiring, and other infrastructure.
Best For: Ideal for environments like data centers, where extensive cabling and air distribution are required beneath the floor.
2. Low Profile Raised Floor
Similar in construction to traditional raised floors, low profile systems are distinguished by their reduced height. This system offers a solution similar to traditional raised floors but with less elevation from the subfloor, making it suitable for environments like offices or classrooms where less underfloor space is needed. It provides easier accessibility and reduces the overall impact on floor height, preserving room aesthetics while still offering utility space.

Height: The space between the subfloor and the panels is usually less than 6 inches, making it less obtrusive and easier to integrate into existing spaces without significant elevation.
Best For: Suitable for office spaces or locations where less underfloor space is needed for utilities, but some access is still necessary.
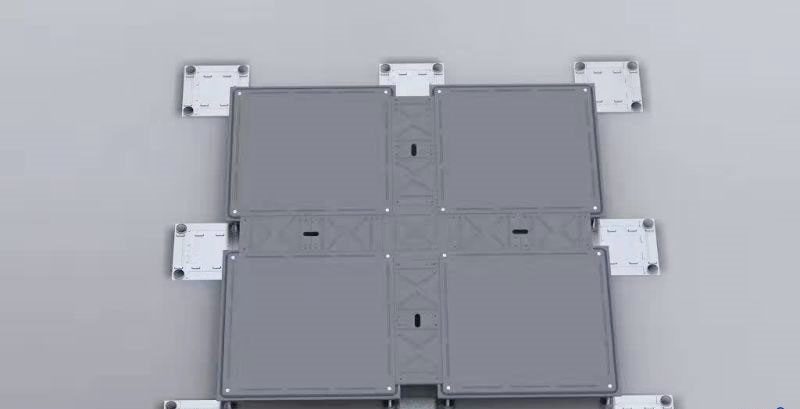
3. Modular Raised Floor
Modular raised floors consist of pre-fabricated units that snap together on-site. This design provides flexibility and ease of installation and reconfiguration.
Flexibility: The modular nature allows for quick assembly and disassembly, facilitating easy access for maintenance and the ability to rearrange the layout as required.
Best For: Frequently used in data centers and offices, particularly where rapid deployment and flexibility are critical.
4. Underfloor Air Distribution (UFAD) System
UFAD systems integrate air distribution into the raised floor, using the plenum beneath the panels as a duct. Floor panels in these systems typically feature integrated air diffusers.
Functionality: This setup allows for efficient distribution of conditioned air directly into the occupied space, enhancing thermal comfort and energy efficiency.
Best For: Commonly implemented in commercial buildings, such as offices and conference centers, where improved indoor air quality and energy savings are priorities.
The choice of installation method for raised floors depends on the specific requirements of the project, including the type of building, the intended use of the space, and future flexibility needs.
Raised Access Floor Types in Applications
Raised floors are versatile, supporting various indoor and outdoor applications by providing easy access to hidden services and the ability to adapt to technological and organizational changes.
1. Indoor Raised Floors
- Data Centers: Need extensive cabling and cooling systems, which can be easily housed and accessed via traditional raised flooring.
- Offices: Benefit from the aesthetic and functional flexibility of low profile and modular raised floors, allowing for easy reconfiguration and maintenance of electrical and data systems.
- Libraries and Educational Facilities: Supports modern educational tools and connectivity needs, while allowing easy reconfigurations.
- Retail Spaces: Facilitates quick modifications in electrical and IT setups, adapting to changing retail layouts and tenant requirements.
- Medical Facilities: In areas like imaging rooms, raised floors provide a platform for heavy equipment and can be designed to reduce interference from vibrations and electromagnetic fields.
- Control Rooms: Essential for managing extensive wiring and providing quick access to underfloor systems without disrupting operations.
- Airports and Train Stations: Facilitates the management of high volumes of cables and provides easy access for maintenance without major disruptions to operations.
- Museums and Exhibition Halls: Offers the flexibility to change exhibits and displays frequently with minimal impact on the existing structure.
2. Outdoor Raised Floors
- Terraces and Rooftops: Raised floors can be used to level uneven surfaces, improve drainage, and conceal services like water and electrical lines.
- Exterior Paths and Gathering Areas: Provides a stable and durable surface capable of withstanding environmental elements while hiding necessary infrastructure.
Which Type of Raised Floor To Choose?
Here are the considerations for choosing Raised Floors:
- When selecting a raised floor system, consider the following:
- Load Capacity: Ensure the system can support the intended equipment and foot traffic.
- Moisture Resistance: Particularly important for outdoor or humid environments.
- Acoustic Properties: Necessary in quiet environments like libraries or offices.
- Fire Resistance: Crucial for ensuring safety in all building types.
The choice of a raised floor system and its installation method greatly depends on the specific needs of a facility, including space usage, structural requirements, and future flexibility. By carefully considering these factors, facility managers and designers can ensure that the raised floor system not only meets the current demands but also adapts to future changes and technological advancements. Whether for indoor or outdoor applications, HUIYA raised access floor systems provide an efficient, adaptable, and aesthetically pleasing solution to manage space and infrastructure. Want to get the best techinal flooring solution for your project with budget cost? Contact us now!
Huiya Real-Time News
Huiya Real-Time News is dedicated to providing you with the latest and most authoritative information on the raised flooring industry.
We provide 24/7 updates on industry policy interpretations, market trend analysis, company news.
MORE DOWNLOADS

GENERAL CATALOGUE

HUIYA INTRODUCTION

HUIYA GREEN LABEL
CAD/BIM FULL STEEL
APPLICATION SCENARIOS